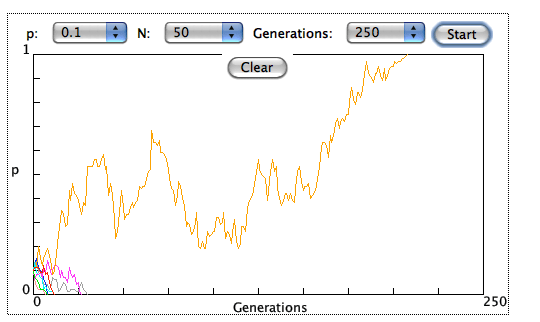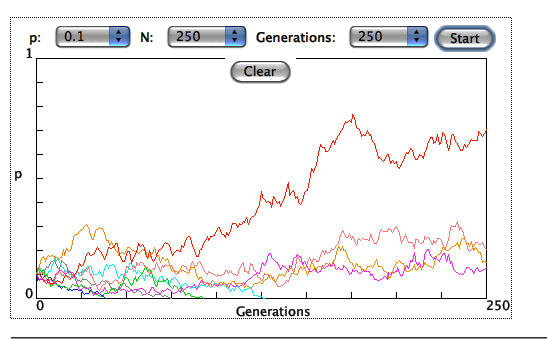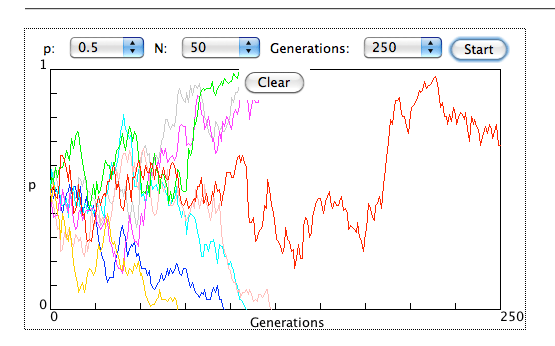
GENETIC DRIFT
A great simulation to help you understand genetic drift.
https://hescgi.oit.ncsu.edu/mit-eve.html or
https://www.merlot.org/merlot/viewMaterial.htm?id=80800
There are two special cases of genetic drift, sampling error and founder effect.
http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/samplingerror_01 and
http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/bottlenecks_01
What are the differences between founder efffects and bottlenecks?
A look at a real life example of where genetic drift through founder effects explains the prevalence of the disease.
http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/medicine_05
Why is Huntington's chorea so prevalent in the lake Maracaibo community?
What other factors are important to understanding the high frequency of this disease besides the influence of founder effect?
Selection or drift?
Determine whether natural selection or genetic drift is driving evolution in each of the following cases. Defend your answer.
a. Case one: humans. A storm blows a small ship of Swedish sailors, most blonde with blue eyes, on to an island. The same storm has claimed most of the native males of reproductive age, most with dark hair and brown eyes, who drowned when their fishing boat capsized. Many of the Swedish sailors stay on the island and marry native girls. Two hundred years later, about 30 % of the island children have blue eyes.
b. Case three: fruit flies. Samples were taken from Europe and North American populations of flies. Both show an increase in wing size from south to north. But the European populations lengthened the part of the wing closest to the body, while those in North America extended the outer segment.
c. Case four: bacteria. Over 11 years researchers raised 24,000 generations of E.coli. All 12 of Lenski's cultures experience the same stresses, a daily boom and bust cycle, in which the bacteria are transferred to fresh glucose medium every 24 hours, than undergo 6 hours or so of plenty followed by 18 hours of starvation. All 12 lines have adopted to this regime; they grow about 60% faster than the original lines and are about 2x the size of the original lines. At the genomic level however, the similarities differ. The sequence changes found in different lines were different and had accumulated at different rates leading to conspicuous and significant discrepancies between genomic evolution and its visible effects.
A real life example where both are suspected:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/news/131211_bottlenecks
Breast cancer paper This is a homework paper.
Monitoring gene frequency can also used to track genetic drift.